Obligations owed to other companies and people are considered liabilities and can be categorized as current and long-term liabilities. Liabilities are the amounts of money the company owes to others. Think of liabilities as obligations — the company has an obligation to make payments on loans or mortgages or they risk damage to their credit and business. On 28 January, merchandise costing $5,500 are destroyed by fire. The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20.
Accounting equation: More examples and explanation
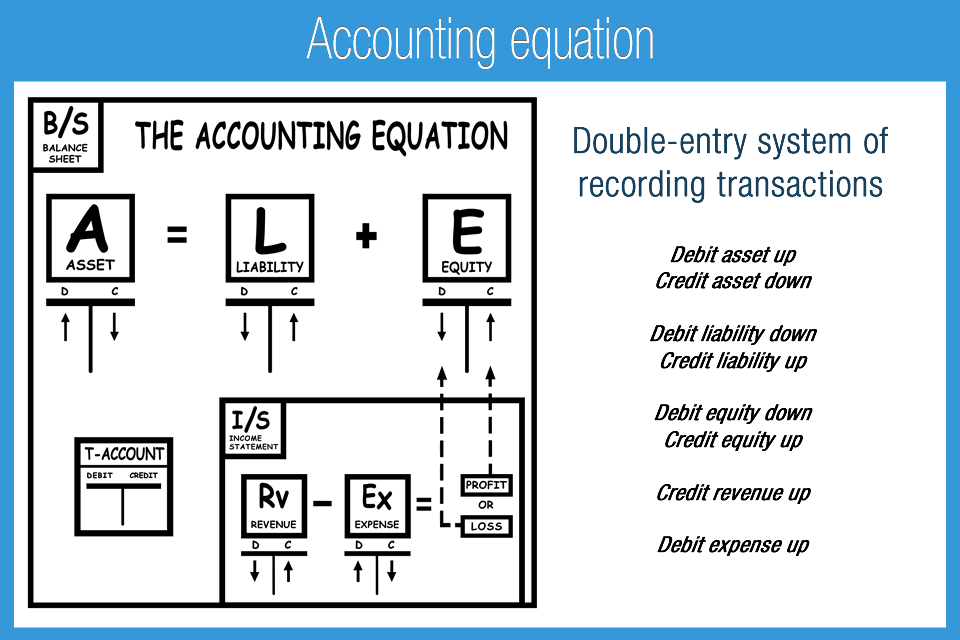
Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. The double-entry practice ensures that the accounting equation always remains balanced, meaning that the left-side value of the equation will always match the right-side value. The accounting equation focuses on your balance sheet, which is a historical summary of your company, what you own, and what you owe. There are different categories of business assets including long-term assets, capital assets, investments and tangible assets.
Assets, Liabilities, And Equity
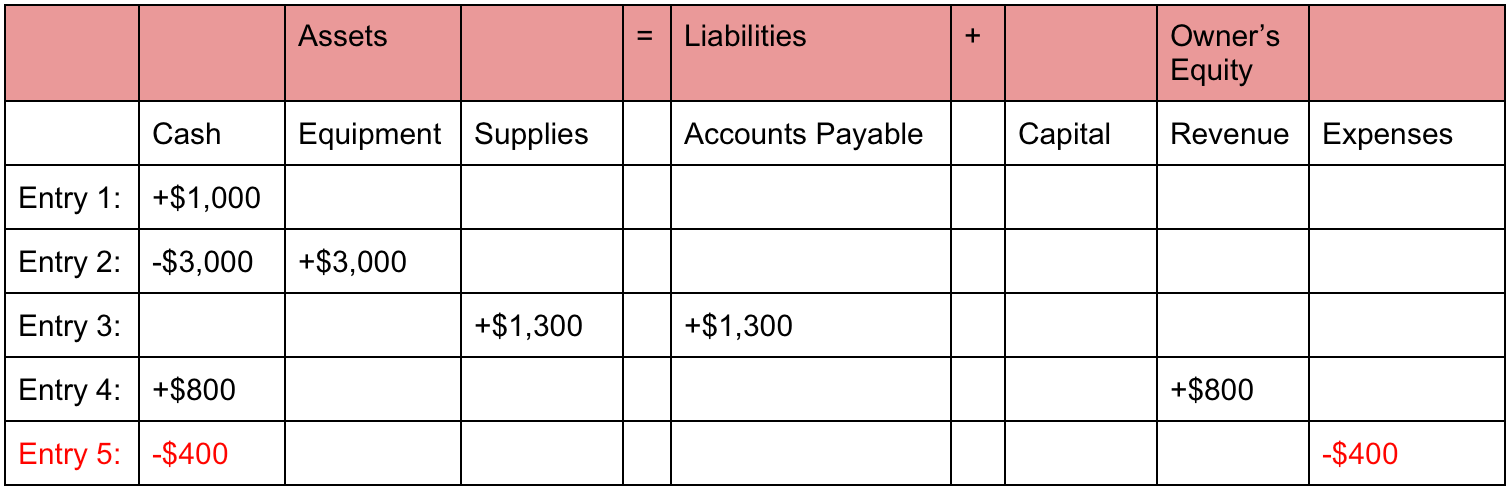
- This transaction would reduce an asset (cash) and a liability (accounts payable).
- The merchandise would decrease by $5,500 and owner’s equity would also decrease by the same amount.
- For every business, the sum of the rights to the properties is equal to the sum of properties owned.
- As you can see, no matter what the transaction is, the accounting equation will always balance because each transaction has a dual aspect.
The accounting equation nonetheless always stays in balance. We know that every business holds some properties known as assets. The claims to the assets owned by a business entity are primarily divided into two types – the claims of creditors and the claims of owner of the business.
Shareholders’ Equity
The income statement is the financial statement that reports a company’s revenues and expenses and the resulting net income. While the balance sheet is concerned with one point in time, the income statement covers a time interval or period of time. The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. In above example, we have observed the impact of twelve different transactions on accounting equation. Notice that each transaction changes the dollar value of at least one of the basic elements of equation (i.e., assets, liabilities and owner’s equity) but the equation as a whole does not lose its balance.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets. So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity).
introduction to accounting information systems ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced. That is, each entry made on the debit side has a corresponding entry (or coverage) on the credit side. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. That is, each entry made on the Debit side has a corresponding entry on the Credit side.
The cost of this sale will be the cost of the 10 units of inventory sold which is $250 (10 units x $25). The difference between the $400 income and $250 cost of sales represents a profit of $150. The inventory (asset) will decrease by $250 and a cost of sale (expense) will be recorded.
Still, you’ll likely see this equation pop up time and time again. However, equity can also be thought of as investments into the company either by founders, owners, public shareholders, or by customers buying products leading to higher revenue. The difference between the sale price and the cost of merchandise is the profit of the business that would increase the owner’s equity by $1,000 (6,000 – $5,000). On 2 January, Mr. Sam purchases a building for $50,000 for use in the business. The impact of this transaction is a decrease in an asset (i.e., cash) and an addition of another asset (i.e., building).
Said a different way, liabilities are creditors’ claims on company assets because this is the amount of assets creditors would own if the company liquidated. If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity). The Accounting Equation is a vital formula to understand and consider when it comes to the financial health of your business. The accounting equation is a factor in almost every aspect of your business accounting. Assets typically hold positive economic value and can be liquified (turned into cash) in the future.
That’s why you’re better off starting with double-entry bookkeeping, even if you don’t do much reporting beyond a standard profit and loss statement. While the accounting equation goes hand-in-hand with the balance sheet, it is also a fundamental aspect of the double-entry accounting system. The third part of the accounting equation is shareholder equity. The revenue a company shareholder can claim after debts have been paid is Shareholder Equity. In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash.




Leave a Comment